Why Predictive Maintenance is gaining adoption in the Paper Industry

The pulp and paper industry has been steadily experiencing a decline in demand for graphic papers used for newsprint, printing, and writing. In a digital-first economy, paper can very well be seen as an obsolete commodity and the growth numbers of past years are nothing but strong evidence of the same. However, as some paper applications decline, others are growing.
Paper packaging is replacing plastics at a fast pace, while specialty paper is gaining popularity in niche markets. Resultantly, thousands of paper production units around the world are adapting their production environments to cater to this transforming demand. There’s an increased focus on optimal utilization of resources, re-integrating waste products into processes, and finding sustainable ways to ensure asset reliability.
Predictive maintenance can play a pivotal role in these changing industry-wide objectives, and here’s how:
Predictive maintenance in Paper Industry
Several rotating equipments are utilized in industrial paper production that requires continuous upkeep and availability. Any undiagnosed machine faults or failures can surmount equipment breakdown and unplanned process downtime. Not only can this mean increased production costs and an unsafe work environment, but it could also mean a disrupted supply chain and unhappy customers.
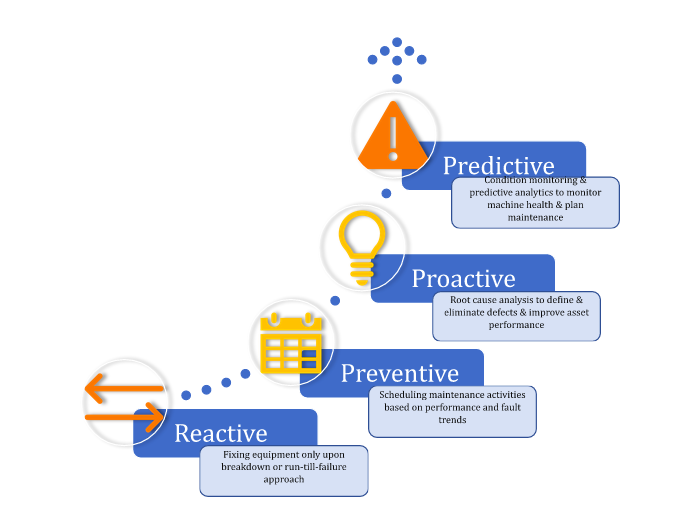
To manage such contingencies, most paper producers rely on preventive or scheduled maintenance, organizing planned production downtimes to carry out maintenance activities and machine part replacements. While this approach reduces the likelihood of factory floor mishaps or sudden machine breakdowns, it does nothing to reduce production downtime. The preventive maintenance approach also leads to a decrease in the remaining useful life (RUL) of assets under deployment and increases the total maintenance cost.

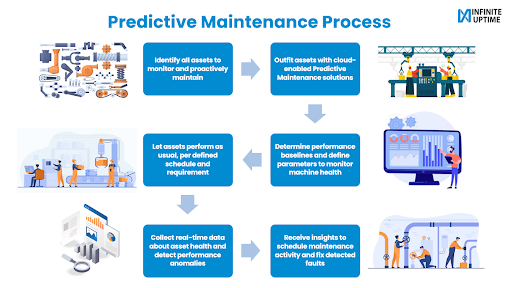
This is why the paper manufacturing plants of the future are slowly but surely adopting a predictive maintenance strategy and shifting away from preventive maintenance. Predictive maintenance (PdM) is a maintenance approach that uses cloud-enabled technologies to monitor diverse assets involved in paper production in real time.
With predictive maintenance, maintenance managers and plant heads can proactively track machine health, estimate the maintenance needs of all deployed assets, and support maintenance decision-making.
Benefits of Predictive Maintenance and Digital Reliability Solutions.
Predictive maintenance relies on continual monitoring of equipment conditions through sophisticated technologies that are IoT-enabled. Technologies such as infrared thermography, vibration analysis, oil analysis, and acoustic monitoring are deployed to collect equipment condition data. The data thus collected is analyzed to detect any deviation in asset performance or irregularities that are otherwise impossible to detect without sophisticated equipment.

The adoption of PdM in paper production contributes toward digital reliability objectives and delivers the following benefits to maintenance and operation teams:
- Maintenance activity is highly targeted in predictive maintenance and only performed when a fault or anomaly is detected. Routinely organized production downtimes and pre-emptive part replacements are not required.
- PdM is increasingly efficient over time and reduces the labor-intensive nature of maintenance activities. Predictive maintenance is also more cost-efficient, reducing the inventory carrying burden for spare parts.
- PdM dashboards also offer machine health insights with digital twin technology, supporting intelligent decision-making for maintenance planning and procurement of machine parts. Consequently, the net cost of assets is effectively reduced as the complete useful life of every machine is utilized before any replacement is done.
- The likelihood of unplanned reactive maintenance is reduced by 70-90% with a predictive approach. Since equipment faults are diagnosed well before the actual functional failure, organized maintenance events can help avoid process disruption and reactive efforts.
- Critical equipment problems and underlying causes of diminishing productivity can be accurately identified with predictive maintenance. As a result, a higher network system reliability can be achieved in a cost-efficient manner.
Critical PdM Applications in Paper Industry
Given the numerous benefits of predictive maintenance, its adoption across the paper and pulp industry seems only natural. But with cost optimization as an important driving force for all strategic planning within the sector, it’s important to identify the critical applications of predictive maintenance and plan a systematic adoption.
The following equipment and machine groups that play a significant role in the paper production process are the most important applications of predictive maintenance solutions in the paper industry:

Several machine groups utilized in paper production have a complex design, making manual monitoring and intervention difficult. Therefore, for each equipment application, the digitization points need to be carefully identified and validated for condition monitoring. With real-time vibration monitoring and predictive analytics, commonly occurring faults can be proactively diagnosed, such as:
- Misalignment
- Unbalance
- Bearing faults
- Structural Looseness
- Gear Defects
- Friction (lack of lubrication)
The maintenance teams can then organize OEM inspections on focused locations and fix or replace machine components that are suffering from a particular fault. The resultant reduction in unplanned downtime and improved machine health can translate into a stronger bottom line and help paper manufacturers develop a true competitive advantage.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, for the paper industry, automation and digitization initiatives have to be driven by the ultimate objective of achieving better cost efficiencies and operational excellence. Predictive maintenance can significantly reduce production and maintenance costs and improve process hygiene across any paper production unit.
With real-time data analytics and access to intelligent insights about machine conditions, PdM can empower maintenance and operation teams more than ever. This is precisely why; global paper manufacturers are adopting predictive maintenance solutions for making their plants more reliable and efficient.
Infinite Uptime’s digital reliability solutions suit specific industry needs and provide advanced analytics to support maintenance and minimize unplanned downtime. Get in touch with our experts or book a demo now to understand how our solutions fit your plant.